The promising news is coming out of Australia in the renewable energy sector. 2018 shows that all sources of renewable energy, including solar energy, pumped hydro, and wind power, are becoming more accessible and are gradually overtaking the use of coal.
Solar energy throughout Australia is not just for the individual homeowner. However, it is important to note that Australians have the largest number of home rooftop solar units globally. In addition, there are solar farms currently under construction, and plans are in place for them to be used to supply electricity to communities across the country.
Continue reading to learn more about the encouraging developments of renewable energy.
Solar Energy
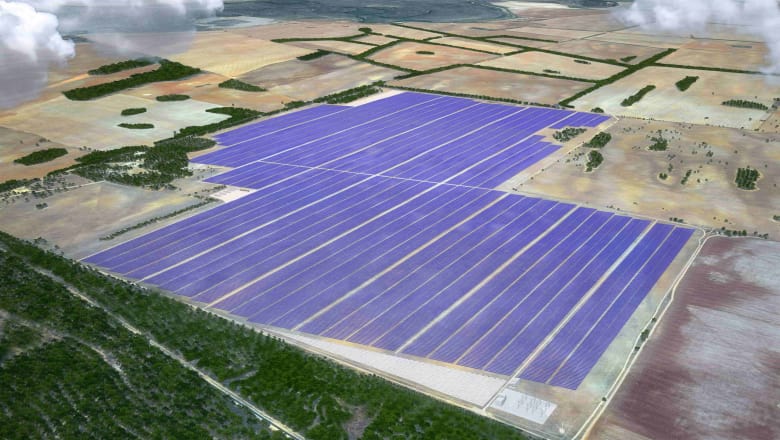
In New South Wales, a large-scale solar farm is being built by Maoneng Australia and Decmil, called “Sunraysia.” Once operational, it will be the largest of its kind in the southern hemisphere, producing 530,000 watts of power each year. Three additional projects are being planned by companies Equis Energy, Lyon Group, and Photon Energy.
National Energy Guarantee
Australian lead scientist Alan Finkel stated in his 2017 review that by 2030 Australia should be on track to have 42% renewable resources providing electricity with coal on the decline. The Australian government is working on a National Energy Guarantee that incorporates all energy sources in a two-part approach of a reliability guarantee and emissions. The NEG has a goal to provide affordable, reliable energy to households and businesses in Australia.
The National Energy Guarantee plans to support 12 large-scale solar farms being built, changing the use of the Kidson, Queensland mine to a hydro and solar facility, and research the possibility of using pumped seawater at the Cultana site in South Australia.
Hydropower
The National Energy Guarantee also plans to expand the “Snowy 2.0” project, a large-scale hydropower operation in the Snowy Mountains. The hydropower is pumped into a storage battery, the largest of its kind in the southern hemisphere. This harnessed power will add 350,000-megawatt-hours of energy into the Australian power grid, lowering emissions and increasing the electricity supply’s reliability.
Wind Power
According to the NEG report, wind and solar costs have dropped to all-time lows in the past decade, up to 50 percent lower. As of 2016, wind power in Australia produced 30.8% of the clean energy and 5.3% of Australia’s total power supply. The turbines currently used are more efficient than older models and are a low-cost renewable energy source. With improvements in technology and capturing power from alternate sources, Australia is on its way to becoming an example for other countries on how to reduce emissions and have a long-term plan in place.
Reliance On Coal
Historically, Australia has been highly dependent on coal. With the recent Paris Agreement, there are now plans for coal to be removed as the number one source as other renewable sources are supported and funded by both the government and private sectors. The catch is that coal is such a large natural resource for Australia that it’s exported to nearby India and China. With the money and big business involved, it will take a massive overhaul of the status quo to see a great reduction in coal mining.
With renewable energy and “going green” in the media more and more, there is hope that governments, businesses, and citizens can put not only words but also action towards lowering greenhouse gas emissions for a better future. The time is now to make the changes that will improve the planet for future generations.